Depression

Transdiagnostic Processes
Disqualifying Others
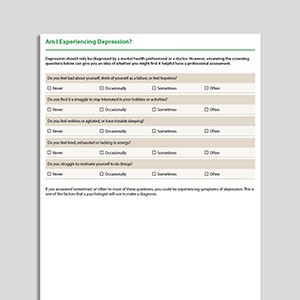
Am I Experiencing Depression?
Perspective-Taking
Overgeneralization
Arbitrary Inference
Exercise For Mental Health
Psychology Tools For Living Well
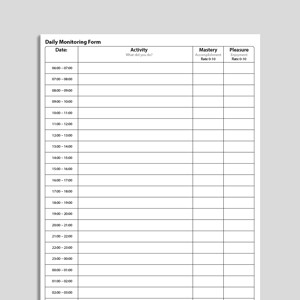
Daily Monitoring Form
Activity Selection
Mindfulness In Everyday Life (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Breath (Long Version) (Audio)
Mindfulness Of Sounds And Thoughts (Audio)
Thinking Versus Sensing (Audio)
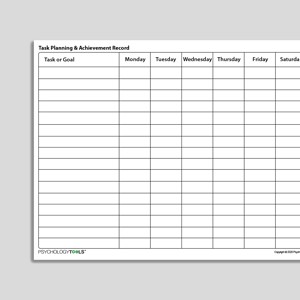
Task Planning And Achievement Record
What Does Exercise Do For the Mind And Body?
Mindful Attention (Audio)
Raisin Exercise (Audio)
Rumination Diary (Archived)
Self-Criticism Self-Monitoring Record (Archived)
Things To Do List
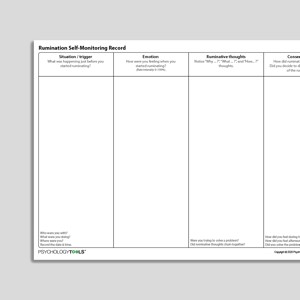
Rumination Self-Monitoring Record (Archived)
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
- Valued Living Questionnaire (Version 2) | Wilson, Groom | 2002
-
Ruminative responses scale
| Treynor, Gonzalez, Nolen-Hoeksema | 2003
- Scale
-
Clinically Useful Depression Outcome Scale (CUDOS)
| Zimmerman, Chelminski, McGlinchey, Posternak | 2008
- Scale
- Zimmerman, M., Chelminski, I., McGlinchey, J. B., & Posternak, M. A. (2008). A clinically useful depression outcome scale. Comprehensive psychiatry, 49(2), 131-140.
-
Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale
| Zung | 1965
- Scale
- Reference Zung, W. W. (1965). A self-rating depression scale. Archives of General Psychiatry, 12(1), 63-70.
-
Severity Measure For Depression – Adult (Adapted from the Patient Health Questionnaire–9 (PHQ-9))
| APA (Spitzer, Williams, Kroenke and colleagues)
- Scale – Adult
- Scale – Child Age 11-17
-
Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9)
| Kroenke, Spitzer | 2002
- Scale phqscreeners.com
- Kroenke, K., & Spitzer, R. L. (2002). The PHQ-9: a new depression diagnostic and severity measure. Psychiatric annals, 32(9), 509-515.
-
Montgomery & Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS)
| Montgomery, Asberg | 1979
- Scale
- MADRS Score Card
- Montgomery, S.A., Asberg, M. (1979). A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry, 134 (4): 382–89.
-
Hamilton Rating Scale For Depression (HAM-D)
| Hamilton | 1960
- Scale
- Hamilton M. (1960). A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 23, 56–62.
-
Edinburgh Post Natal Depression Scale (EPDS)
| Cox, Holden, Sagovsky | 1987
- Scale
- Cox, J. L., Holden, J. M., & Sagovsky, R. (1987). Detection of postnatal depression: development of the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 150(6), 782-786.
Case Conceptualization / Case Formulation
- Developing and using a case formulation to guide cognitive behaviour therapy | Persons | 2015
- Cognitive conceptualisation (excerpt from Basics and Beyond) | J. Beck
Guides and workbooks
- Mood And Substance Use | NDARC: Mills, Marel, Baker, Teesson, Dore, Kay-Lambkin, Manns, Trimingham | 2011
Information Handouts
-
Depression (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What Is Depression?
- What Causes Depression?
- Psychotherapy for Depression
- Vicious Cycle of Depression
- Behavioural Activation: Fun and Achievement
- Fun Activities Catalogue
- Improving How You Feel
- Thinking and Feeling
- Analysing Your Thinking
- Changing Your Negative Thinking
- Unhelpful Thinking Styles
- What Are Core Beliefs?
- Problem Solving
- Staying Healthy
- Grief and Bereavement
Information (Professional)
- Get out of the TRAP and back on TRAC (for rumination and worry) | GoodMedicine
Self-Help Programmes
-
Behavioral Activation For Depression
| Southwark Psychological Therapies Service | 2012
- Introduction to BA for depression
- Monitoring Activity And Mood
- Roadmap: The Activation Plan
- Finding Direction: Values, Flow, And Strengths
- Avoidance And Depression TRAPs
- Thinking Habits
- Next Steps
-
Back from the Bluez (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2003
- Module 1: Overview of Depression
- Module 2: Behavioural Strategies for Managing Depression
- Module 3: The Thinking-Feeling Connection
- Module 4: The ABC Analysis
- Module 5: Unhelpful Thinking Styles
- Module 6: Detective Work and Disputation
- Module 7: The End Result
- Module 8: Core Beliefs
- Module 9: Self-Management
-
Back From The Bluez (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2003
- Module 1: Overview Of Depression
- Module 2: Behavioral Strategies For Managing Depression
- Module 3: The Thinking-Feeling Connection
- Module 4: The ABC Analysis
- Module 5: Unhelpful Thinking Styles
- Module 6: Detective Work And Disputation
- Module 7: The End Result
- Module 8: Core Beliefs
- Module 9: Self Management
Treatment Guide
- Depression In Adults: Treatment And Management (NICE Guideline) | NICE | 2022
- Behavioural activation treatment for depression (BATD) manual | Lejuez, Hopko & Hopko | 2001
- Suicide and self injury: a practitioners guide | Forensic Psychology Practice Ltd | 1999
- Behavioural activation treatment for depression – revised (BATD-R) manual | Lejuez, Hopko, Acierno, Daughters, Pagoto | 2011
- Metacognitive Training For Depression (D-MCT) Manual | Jelinek, Schneider, Hauschild, Moritz | 2023
-
Metacognitive Training For Depression
| Jelinek, Hauschildt, Moritz & Schneider | 2022
- Module 1: Thinking and reasoning 1
- Module 2: Memory
- Module 3: Thinking and reasoning 2
- Module 4: Self-worth
- Module 5: Thinking and reasoning 3
- Module 6: Behaviors and strategies
- Module 7: Thinking and reasoning 4
- Module 8: Perception of feelings
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy for depression in young people: a modular treatment manual | Orygen | 2015
- Group therapy manual for cognitive behavioral treatment of depression | Muñoz, Miranda | 1993
- CBT For Depression In Veterans And Military Service Members – Therapist Manual | Wenzel, Brown, Carlin | 2011
- Cognitive behaviour therapy for depression in young people: manual for therapists | Improving Mood with Psychoanalytic and Cognitive Therapies (IMPACT) Study CBT Sub-Group | 2010
- Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy (CBT) Group Program For Depression | Milner, Tischler, DeSena, Rimer
- Manual for group cognitive-behavioral therapy of major depression: a reality management approach (Instructor’s manual) | Muñoz, Ippen, Rao, Le, Dwyer | 2000
- Individual therapy manual for cognitive-behavioural treatment of depression | Ricardo Muñoz, Jeanne Miranda | 1996
- Depression In Adults: Recognition And Management | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines | 2009
Worksheets
-
Depression (Worksheets)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- Symptoms of Depression
- Behavioural Activation
- My Behavioural Antidepressants
- Weekly Activity Schedule
- Weekly Goals Record
- Making the Connection (Between Thoughts and Feelings)
- Thought Diary 1
- Thought Diary 2
- Thought Diary 3
- Thought Diary (Tri-fold)
- Core Beliefs Worksheet
- Healthy Me
- Goal Setting (End of Therapy)
Recommended Reading
- Behavioural activation treatment for depression: returning to contextual roots | Jacobson, Martell, Dimidjian | 2001
What Is Depression?
Signs and Symptoms of Depression
To meet DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder an individual must have experienced five of the following symptoms for at least two weeks:
- a depressed mood that is present most of the day, nearly every day
- diminished interest in activities which were previously experienced as pleasurable
- fatigue or a loss of energy
- sleep disturbance (insomnia or hypersomnia)
- feelings of worthlessness, self-reproach, or excessive guilt
- a diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness
- recurrent thoughts of death or suicide, or suicidal behavior
- changes in appetite marked by a corresponding weight change
- psychomotor agitation or retardation to a degree which is observable by others
Psychological Models and Theory of Depression
Beck’s cognitive theory of depression (Beck, Rush, Shaw, & Emery, 1979) forms the basis for cognitive behavioral approaches for the treatment of depression. Beck’s theory proposes that there are different levels of cognition that can be dysfunctional in depression: core beliefs, rules and assumptions, and negative automatic thoughts. CBT aims to balance negatively biased cognition with more rational and accurate thoughts, beliefs, and assumptions. CBT also systematically aims to increase levels of rewarding activity.
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) proposes that distress, including symptoms of depression, are the result of psychological inflexibility (Hayes, Luoma, Bond, Masuda, & Lillis, 2006). Indicators of psychological inflexibility include:
- ‘buying in’ to negative thoughts and narratives;
- engaging in worry or rumination that takes us away from the present moment;
- losing contact with our values—what is important to us.
Evidence-Based Psychological Approaches for Working with Depression
Many psychological therapies have an evidence base for working with depression:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Behavioral activation (BA)
- Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT)
- Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) for preventing relapse
- Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
Resources for Working with Depression
Psychology Tools resources available for working therapeutically with depression may include:
- psychological models of depression
- information handouts for depression
- exercises for depression
- CBT worksheets for depression
- self-help programs for depression
References
- Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. New York: Guilford Press.
- Hayes, S. C., Luoma, J. B., Bond, F. W., Masuda, A., & Lillis, J. (2006). Acceptance and commitment therapy: Model, processes and outcomes. BehaviourResearch and Therapy, 44(1), 1–25.