Download or send
Tags
Languages this resource is available in
Problems this resource might be used to address
Techniques associated with this resource
Mechanisms associated with this resource
Introduction & Theoretical Background
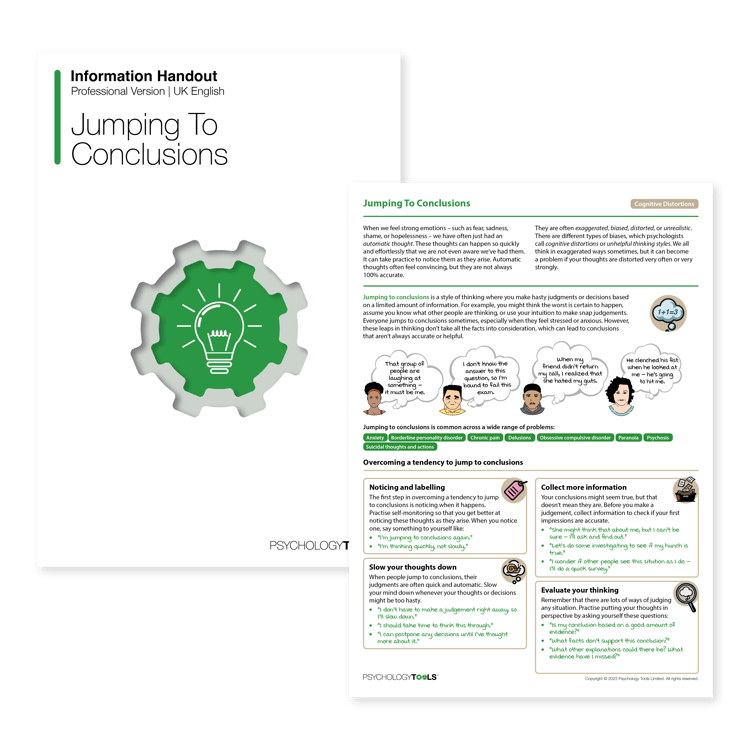
A brief introduction to cognitive distortions
Cognitive distortions, cognitive biases, or ‘unhelpful thinking styles’ are characteristic ways in which our thoughts can become biased (Beck, 1963). As conscious beings we are always interpreting the world around us, trying to make sense of what is happening. Sometimes our brains take ‘short cuts’ and we think things that are not completely accurate, and different cognitive short cuts result in different kinds of bias or distortions in our thinking. Sometimes we might jump to the worst possible conclusion (“this rough patch of skin is cancer!”), at other times we might blame ourselves for things that are not our fault (“If I hadn’t made him angry he wouldn’t have hit me”), and at other times we might rely on intuition and jump to conclusions (“I know that they all hate me even though they’re being nice”).
Different cognitive biases are associated with different clinical
Therapist Guidance
“Many people jump to conclusions, and it sounds as though it might also be the case for you. Would you be willing to explore it with me?”
Clinicians might begin by providing psychoeducation about jumping to conclusions and automatic thoughts more generally. Consider sharing some of these important details:
- Automatic thoughts spring up spontaneously in our minds, usually in the form of words or images.
- They are often on the ‘sidelines’ of our awareness. With practice, we can become more aware of them. It is a bit like a theatre – we can bring our automatic thoughts ‘centre stage’.
- Automatic thoughts are not always accurate: just because you think something, it doesn’t make it true.
- Automatic thoughts are often inaccurate in characteristic ways. One common type of bias in automatic thoughts is ‘jumping to conclusions’ – we sometimes make hasty judgments and decisions based on limited evidence and
References And Further Reading
- Beck, A. T. (1963). Thinking and depression: I. Idiosyncratic content and cognitive distortions. Archives of General Psychiatry, 9, 324-333. DOI: 10.1001/archpsyc.1963.01720160014002.
- Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. Guilford Press.
- Beck, J. S. (1995). Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond. Guilford Press.
- Bensi, L., & Giusberti, F. (2007). Trait anxiety and reasoning under uncertainty. Personality and Individual Differences, 43, 827-838. DOI: 10.1016/j.paid.2007.02.007.
- Blake, E., Dobson, K. S., Sheptycki, A. R., & Drapeau, M. (2016). The relationship between depression severity and cognitive errors. American Journal of Psychotherapy, 70, 203-221. DOI: 10.1176/appi.psychotherapy.2016.70.2.203.
- Burns, D. D. (2020). Feeling great: The revolutionary new treatment for depression and anxiety. PESI Publishing.
- Byrne, A., & Eysenck, M. W. (1993). Individual differences in positive and negative interpretive biases. Personality and Individual Differences, 14, 849-851. DOI: 10.1016/0191-8869(93)90100-H.
- Clark, D. A., & Beck, A. T. (2010). Cognitive therapy