Forgiveness

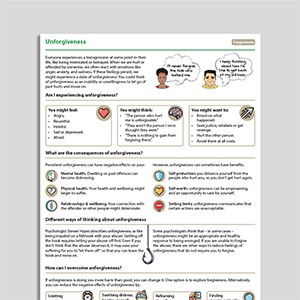
Unforgiveness
Forgiveness
Forgiveness Methods
Unforgiveness – The Hook
What Forgiveness Is Not
Forgiveness Quotes
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Guides and workbooks
- Conversations About Forgiveness (Workbook)
Information Handouts
- Healing through forgiveness | Rindfleisch | 2016
Information (Professional)
- The Enright Model of Psychological Forgiveness | Phillip Sutton
- Enright Forgiveness Process Model | International Forgiveness Institute
Treatment Guide
- The courage to forgive: educating elementary school children about forgiveness | Suzanne Freedman, Robert Enright | 2021
Recommended Reading
- Baskin, T. W., & Enright, R. D. (2004). Intervention studies on forgiveness: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Counseling & Development, 82(1), 79-90
- Enright, R. D., Fitzgibbons, R. P. (2000). Helping clients forgive: An empirical guide for resolving anger and restoring hope. Washington DC: American Psychological Association
- McCullough, M. E., vanOyen Witvliet, C. (2009). The psychology of forgiveness, in Snyder, C. R., & Lopez, S. J. eds, Oxford handbook of positive psychology. Oxford University Press, USA
What Is Forgiveness?
Forgiveness is a complicated term that is frequently misunderstood. Forgiving encompasses:
- a willingness to abandon one’s right to resentment, negative judgment, and negative behavior toward one who acted unjustly; and
- the voluntary fostering of the undeserved qualities of compassion, generosity, and sometimes even love toward the one who offended.
What Forgiveness Is Not…
Forgiveness is often misunderstood to mean reconciling, forgetting, pardoning, and/or accepting. Forgiving is separate from justice—one can forgive but still seek recognition and justice.
Freedman and Enright (2017) quote a survivor of domestic violence who clarifies some of the dimensions of forgiveness:
“Upon forgiving, I have not forgotten what happened. In remembering I make different choices in my intimate relationships. I do not condone what was done to me. It was morally wrong and undeserved. This forgiveness is not pardon, for I do not excuse his behavior or pretend it never occurred. My process of forgiveness was not reconciliation. In fact, mine was the opposite. It is a fracture that will never be mended.”
The Process Model of Forgiveness
Enright’s model of forgiveness identifies four phases.
- Uncovering phase: In which the injured person comes to an awareness of their hurt and feelings associated with how they were wronged.
- Decision phase: In which the injured person recognizes that the way in which they have been coping is no longer effective and begins to explore forgiveness as an option for healing. This phase involves an exploration of what forgiveness is and is not.
- Work phase: In which the injured person actively engages in a process of understanding their offender, developing compassion and empathy, and absorbing the pain of their injury instead of passing it on to others.
- Outcome or discovery phase: In which the injured person attempts to find meaning in their suffering, and realizes that giving the gift of forgiveness is healing for themselves.
References
- Enright, R. D., & Fitzgibbons, R. P. (2000). Helping clients forgive: An empirical guide for resolving anger and restoring hope. American Psychological Association.
- Enright, R. D., & Fitzgibbons, R. (2015). Forgiveness therapy: An empirical guide for resolving anger and restoring hope. Washington, DC: APA Books.
- Freedman, S., & Enright, R. D. (2017). The use of forgiveness therapy with female survivors of abuse. Journal of Women’s Health Care, 6(3), art. 369. doi: 10.4172/2167-0420.1000369